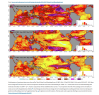
Connectivity of protected areas (PAs) is needed to ensure the long-term persistence of biodiversity and ecosystem service delivery. The Convention on Biological Diversity agreed in 2010 to have 17% of land covered by wellconnected PA systems by 2020 (Aichi Target 11). We here globally assess, for all countries, the trends in terrestrial PA connectivity every other year from 2010 to 2018 using the ProtConn indicator, which quantifies how well the PA systems are designed to support connectivity. The percentage of protected connected land (ProtConn) has increased globally from 6.5% in 2010 to 7.7% in 2018. Oceania experienced the largest recent increase in PA connectivity, whereas Asia is the only content with a lower ProtConn in 2018 than in 2010. Globally, the relative increase in the percentage of protected connected land (ProtConn) is nearly twice that of the percentage of land under protection (PA coverage), due to clear improvements in the design of PA systems for connectivity in many regions. The connectivity of the PA networks has become more dependent on the permeability of the unprotected landscape matrix in between PAs and on the coordinated management of adjacent PAs with different designations and of transboundary PA linkages. The relatively slow recent increase in PA connectivity globally (2016–2018) raises doubt as to whether connectivity targets will be met by 2020, and suggests that considerable further action is required to promote better-connected PA systems globally, including the expansion of the PA systems to cover key areas for connectivity in many countries and regions