Interest in deep-sea mining for copper, cobalt, zinc, manganese and other valuable metals has grown substantially in the last decade and mining activities are anticipated to begin soon.
Environmentalists including Britain’s David Attenborough have called for a ban on deep-seabed mining that would extract resources including copper, cobalt, nickel, zinc, lithium, and rare earth elements from nodules on the ocean floor. The International Seabed Authority (ISA), a U.N.
The public is to be consulted for one week on changes to the seabed mining laws, after a last-minute plea from environmentalists. The Seabed Minerals Amendment Bill 2020 was scheduled to be tabled in Parliament yesterday.
The Cook Islands government will allow miners to prospect for minerals on its seabed, with an eye to commencing mining within five years.
Predicting the Impacts of Mining Deep Sea Polymetallic in the Pacific Ocean
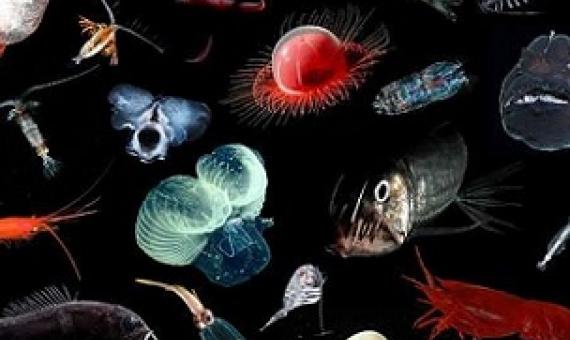
This review represents an analysis of literature addressing the predicted and potential impacts of mining deep sea nodules in the Southwest, Central, and Northeast Pacific. More than 250 scientific and other articles were examined to explore what is known — and what remains unknown — about the risks of nodule mining to Pacific Ocean habitats, species, ecosystems and the people who rely on them. The report details scientifically established risks, including those related to the lack of knowledge surrounding this emerging industry.
A new report analysing over 250 peer reviewed scientific articles finds that the impacts of mining deep sea polymetallic nodules would be extensive, severe, and last for generations, causing essentially irreversible species loss.
The environmental impact of deep-sea mining is only partially known. Also, there is a lack of standards to regulate mining and set binding thresholds for the impact on the local organisms.
On April 20, 2010, the explosion of BP's Deepwater Horizon drilling platform claimed the lives of 11 workers and unleashed a torrent of more than four million barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico.
Sir David Attenborough has urged governments to ban deep sea mining, following a study warning of “potentially disastrous” risks to the ocean’s life-support systems if it goes ahead.
Existing environmental management approaches relevant to deep-sea mining
Deep-sea mining (DSM) may become a significant stressor on the marine environment. The DSM industry should demonstrate transparently its commitment to preventing serious harm to the environment by complying with legal requirements, using environmental good practice, and minimizing environmental impacts. Here existing environmental management approaches relevant to DSM that can be used to improve performance are identified and detailed.