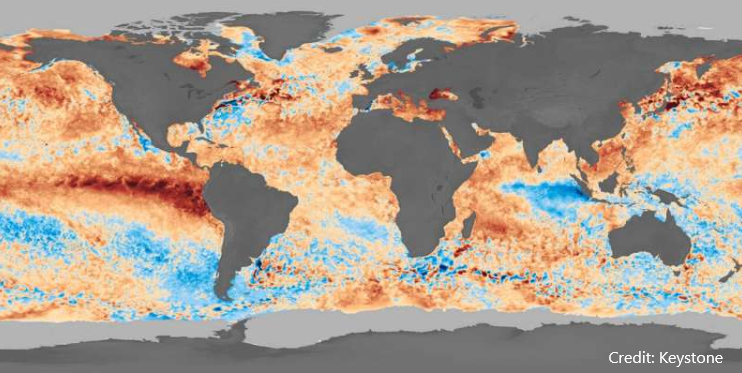
Measurements analyzed by an international research team led by ETH Zurich show that the global ocean absorbed significantly less CO₂ than anticipated during the unprecedented marine heat wave in 2023. The world's oceans act as an important sink for carbon dioxide (CO₂). To date, they have absorbed around a quarter of human-induced CO₂ emissions from the atmosphere, thereby stabilizing the global climate system.
Without this sink, the CO₂ concentration in the atmosphere would be much higher and global warming would have already significantly exceeded the 1.5-degree warming limit. At the same time, the ocean absorbs around 90% of the additional heat from the atmosphere.
Publication














