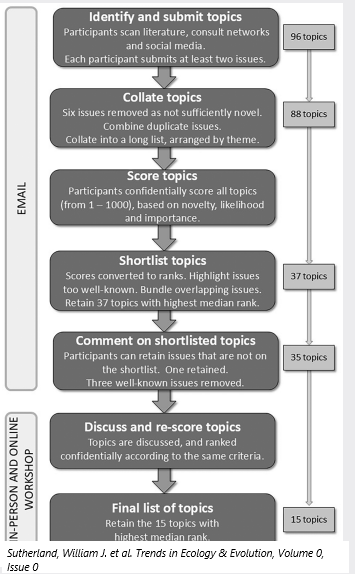
We present outcomes from our 17th horizon scan of issues potentially impacting global biodiversity conservation in the next decade. Issues are novel, or represent a significant step-change in impact, and are currently not well-known or understood within the conservation community. Our panel of 26 scientists, practitioners, and policymakers scored an initial list of 96 issues, discussed the highest ranked 35 issues at a workshop, and identified the 15 top-ranked issues. This year, technology innovations, including low-power optic artificial intelligence (AI) chips and tiny machine learning (TinyML) models, could revolutionize biodiversity monitoring. We highlight impacts from changes in land-use driven by appetite-suppressing pharmaceuticals and the unknown effects of mirror biomolecules. Highlighting these issues may increase awareness of any impacts on global biodiversity conservation.














