Protected Area targets have been set globally, regionally, and sometimes at a country level. During the last decade, the global protected area targets that all country signatories to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) committed to were the CBD's Aichi Biodiversity Targets. Specifically, Aichi Target 11 which stated that:
at least 17 per cent of terrestrial and inland water, and 10 per cent of coastal and marine areas, especially areas of particular importance for biodiversity and ecosystem services, are conserved through effectively and equitably managed, ecologically representative and well connected systems of protected areas and other effective area-based conservation measures, and integrated into the wider landscapes and seascapes by 2020.
The new Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) was adopted in December 2022 at the 15th Meeting of the Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD COP15). CBD country signatories have committed to implementing the protected area target (Target 3) of the new GBF by the year 2030. The text of Target 3 is below:
Ensure and enable that by 2030 at least 30 per cent of terrestrial, inland water, and of coastal and marine areas, especially areas of particular importance for biodiversity and ecosystem functions and services, are effectively conserved and managed through ecologically representative, well-connected and equitably governed systems of protected areas and other effective area-based conservation measures, recognizing indigenous and traditional territories, where applicable, and integrated into wider landscapes, seascapes and the ocean, while ensuring that any sustainable use, where appropriate in such areas, is fully consistent with conservation outcomes, recognizing and respecting the rights of indigenous peoples and local communities including over their traditional territories.
Regionally, the Micronesia Challenge aims to effectively conserve at least 30% of near-shore marine resources and 20% of terrestrial resources across Micronesia by 2020. An example of a country-based target is Fiji that aims to have 30% of reefs protected by 2015 and 30% of waters managed as a marine protected area network by 2020. During the 24th Micronesia Island Forum in 2019, the Leaders recognized the success in the first 15 years of the Micronesia Challenge and endorsed the new Micronesia Challenge 2030 goals to effectively manage 50% of marine resources, including the exclusive economic zone (EEZ), and 30% of terrestrial resources by 2030.
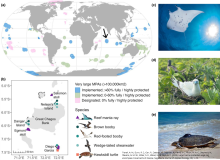
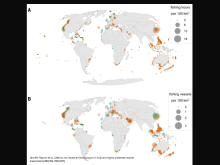
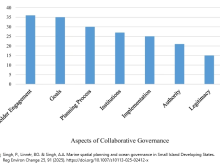
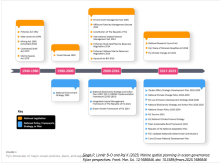
Below are various efforts that have been carried out to assess global and regional progress towards the Aichi protected area targets. The paper by Govan (2009) is the most comprehensive assessment of marine protected areas (MPAs), including all LMMAs in the Pacific Islands. Govan’s data has now been incorporated into the World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA). Several of the papers below attempt to assess progress towards targets which relate to factors such as management effectiveness, biodiversity coverage, governance and finance etc.
As we move closer to 2030, further technical guidance on implementing the new GBF Target 3 that becomes available will be added to the resources section below. Furthermore, the resources section will be updated as needed to include any new papers or guidance related to taking stock of national, regional and global progress in implementing the GBF Target 3.
Making waves: The science and politics of ocean protection
Lubchenco, Jane, and Kirsten Grorud-Colvert. 2015. Making waves: The science and politics of ocean protection. Science Vol.
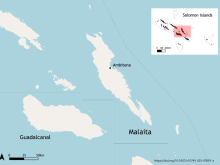
Management of plan for the Ijuw/Anabar wetlands proposed conservation area (PCA) - Republic of Nauru
Marine Areas Beyond National Jurisdictions - What to do?
In June, 2015 the United Nations General Assembly approved a resolution calling for the development of an international legally-binding
Marine protection targets: an updated assessment of global progress
Oonzaier, L. B. and D. Pauly. 2016. Marine protection targets: an updated assessment of global progress. Oryx 50(1), 27–35.